3.2 Results and Discussion of Emulsion PS Modified Adhesives
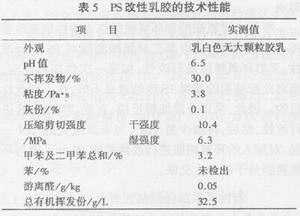
3.2.1 Properties of Emulsion Modified Adhesives as Table 5
3.2.2 Characterization of Graft Copolymers
From the grafting reaction mechanism of polystyrene and unsaturated polar monomer, it is inferred that the reactant should be polystyrene-acrylic acid ester-vinyl acetate graft copolymer with a small amount of unreacted monomers and Grafted polystyrene. We can characterize it from two aspects: on the one hand, by monitoring the bromine number at different stages of the reaction, the copolymerization reaction of the monomer can be seen from the gradual decrease of the bromine value; on the other hand, unreacted monomers in the product are extracted after the completion of the reaction. The infrared absorption spectrum of the remaining sample was measured, and there was a significant C=0 characteristic absorption near 1700 cm. The absence of a C=C absorption peak near 2200 cm clearly indicated that there was indeed a graft copolymer of polystyrene and a mixed monomer in the resultant product. The presence of the substance, the graft copolymerization reaction was successful.
3.2.3 Selection of Low-toxicity Mixed Solvents
The choice of mixed solvent not only determines the cost of the adhesive, but also determines the level of toxicity and its performance. Based on the solubility parameter and the hydrogen bonding index of polystyrene, the mixed solvent is preferable. When the solubility parameter and the hydrogen bonding index of the mixed solvent are similar to those of polystyrene, the polystyrene can be well dissolved. Considering the solubility parameters and considering the toxicity, I chose the ethyl acetate-toluene system as a mixed solvent with low toxicity, low cost, and good solubility. The ratio is 4:1 and the amount is polyphenyl. 1.5 times that of ethylene, and the remaining amount after the reaction was about 25% of polystyrene.
3.2.4 Selection of Modifiers
Because the molecular structure of polystyrene contains a benzene ring group, the flexibility of the link is reduced, the adhesive strength of the adhesive is decreased, and the adhesive layer is hard and brittle. Therefore, it is necessary to add a modifier. The reasons why acrylates and vinyl acetate were selected as modifying monomers were as follows: Acrylates were soft monomers, which gave the copolymers a low glass transition temperature and excellent softness, reduced the film formation temperature and the adhesive layer. The hardness and brittleness increase the peel strength and cold resistance of the adhesive; vinyl acetate is a hard monomer that can increase the strength of the copolymer and reduce the cost. The addition of the plasticizer dioctyl phthalate is used to increase the flexibility of the adhesive, improve the performance of the adhesive, and at the same time shorten the curing time of the adhesive layer.
3.2.5 Influence of Mixed Monomer Dosage on Adhesive Strength
Figure 4 shows the effect of the modifier, that is, the amount of mixed monomer on the shear strength. From the figure, it can be seen that the shear rate of the modifier, which is about 40% of PS, already exceeds the shear strength of the white glue. The monomers were copolymerized and grafted with PS, and polar groups were introduced on the polystyrene chains to modify the PS. Therefore, as the mixed monomers increase, the polar groups on the chain segments increase, so the shear strength gradually increases. When the mixed monomers increase again, the shear strength does not change much. It may sometimes decrease due to the increased degree of cross-linking. Moreover, the higher the cost of the monomer, the higher the loss of the significance of waste utilization, so the monomer accounted for 40% of PS is sufficient.

(to be continued)